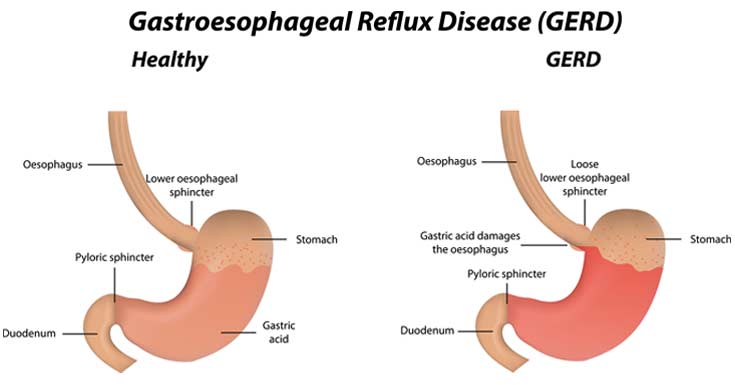
Gastrointestinal, Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD), gastric reflux disease, or acid reflux disease is defined as chronic symptoms or mucosal damage produced by the abnormal reflux in the esophagus.
One in 10 Americans experiences heartburn symptoms at least once a week. Heartburn has different triggers, including certain foods, medications, obesity, or even stress. Acid reflux is common, but chronic acid reflux (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) can become a real problem.
At the entrance to the stomach is a valve called lower esophageal sphincter (LES). The LES should close as soon as food enters the stomach so that no food can splash back up into the esophagus, however, if the LES does not close properly or if it opens often, stomach acid can move into the esophagus and cause heartburn. There are various causes including hiatal hernias, eating foods containing high amounts of acid (citrus, coffee, tomato, chocolate, or spicy or fatty foods), and drinking alcohol.
Typically, GERD is treated with prescription or over the counter medications. These prescriptions can have side effects such as nausea, headache, diarrhea, gas, bloating, constipation, and stomach pain. Cannabinoids can be effective against these side effects, but it can also improve acid reflux in general.
It has been found that “Activation of cannabinoid receptors (CB(1), CB(2) and GPR(55)) produces analgesic effects in several experimental pain models, including visceral pain arising from the gastrointestinal tract” in one study at AstraZeneca R&D Mölndal in Sweden.
At the Department of Experimental Pharmacology at the University of Naples in Italy also conducted research on gastrointestinal problems: “Salvinorin A, the active component of the hallucinogenic herb Salvia divinorum, inhibits intestinal motility through activation of kappa-opioid receptors (KORs). However, this compound may have target(s) other than the KORs in the inflamed gut. Because intestinal inflammation upregulates cannabinoid receptors and endogenous cannabinoids, in the present study we investigated the possible involvement of the endogenous cannabinoid system in salvinorin A-induced delay in motility in the inflamed gut.” The study concluded, “The inhibitory effect of salvinorin A on motility reveals a functional interaction between cannabinoid CB(1) receptors and KORs in the inflamed-but not in the normal-gut in vivo.”